
EN ISO 11611
EN ISO 11611
Protective clothing for welding and allied processes
What do I need to consider when using protective welding clothing?
- All areas of skin not covered by the protective clothing must be protected by additional equipment such as protective bonnet, gloves, hose scarf, etc.
- Work clothing made of easily flammable or easily melting material must not be worn during welding. Burn injuries could be considerably aggravated by this.
- Depending on the work task and welding position, it may also be necessary to wear additional leather aprons, leather gaiters.
- Protective clothing for welders must not be contaminated by oil, grease, oxygen, etc. When cleaning, care must be taken to ensure that the manufacturer's instructions are followed. This is the only way to ensure the effectiveness of the equipment.
- For the selection of protective clothing for welders for different welding activities, Annex A of EN ISO 11611:2015 "Guidance for the selection of the type of protective clothing for welders, Class 1 and 2" shall be used or referred to.

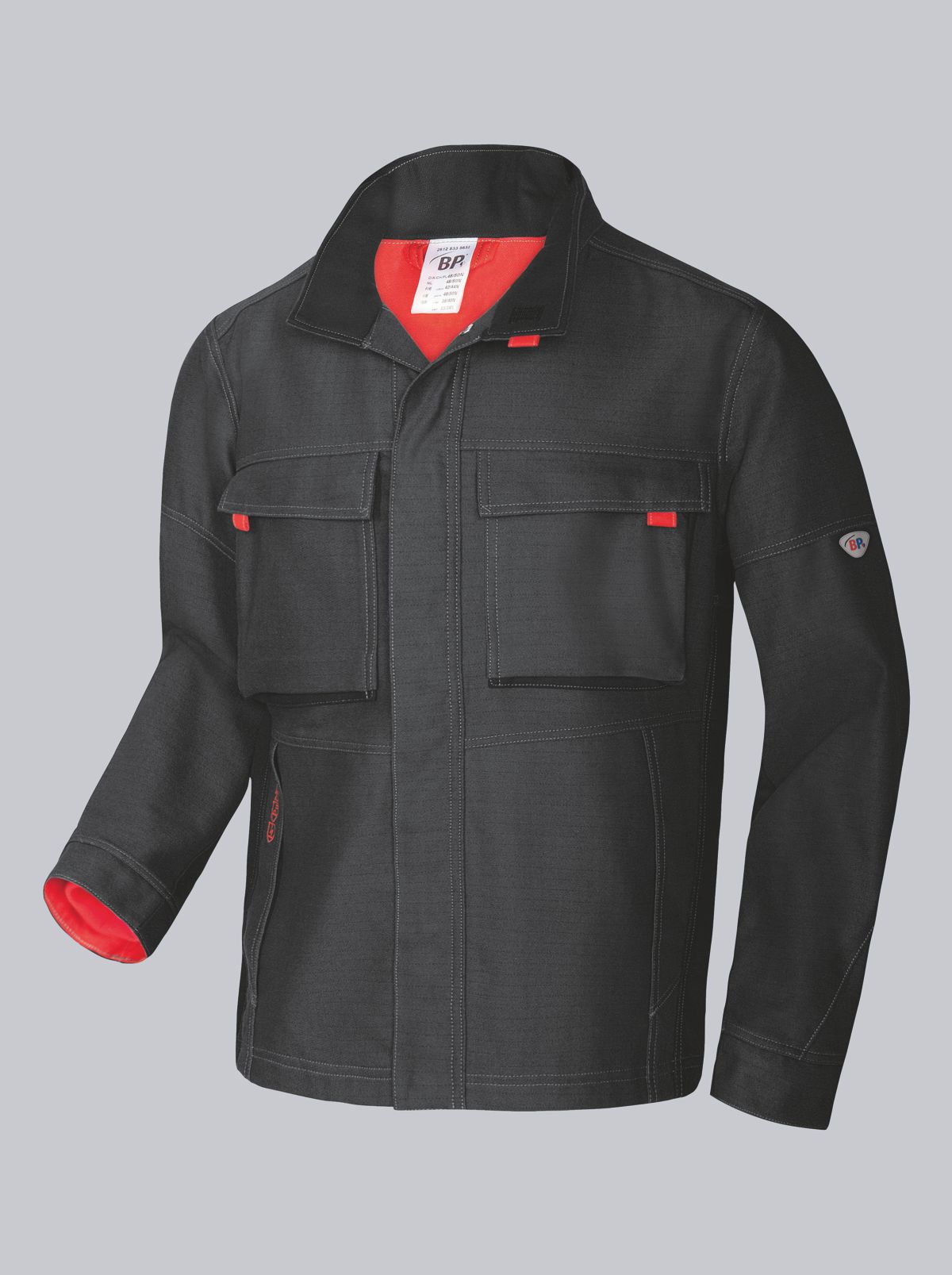
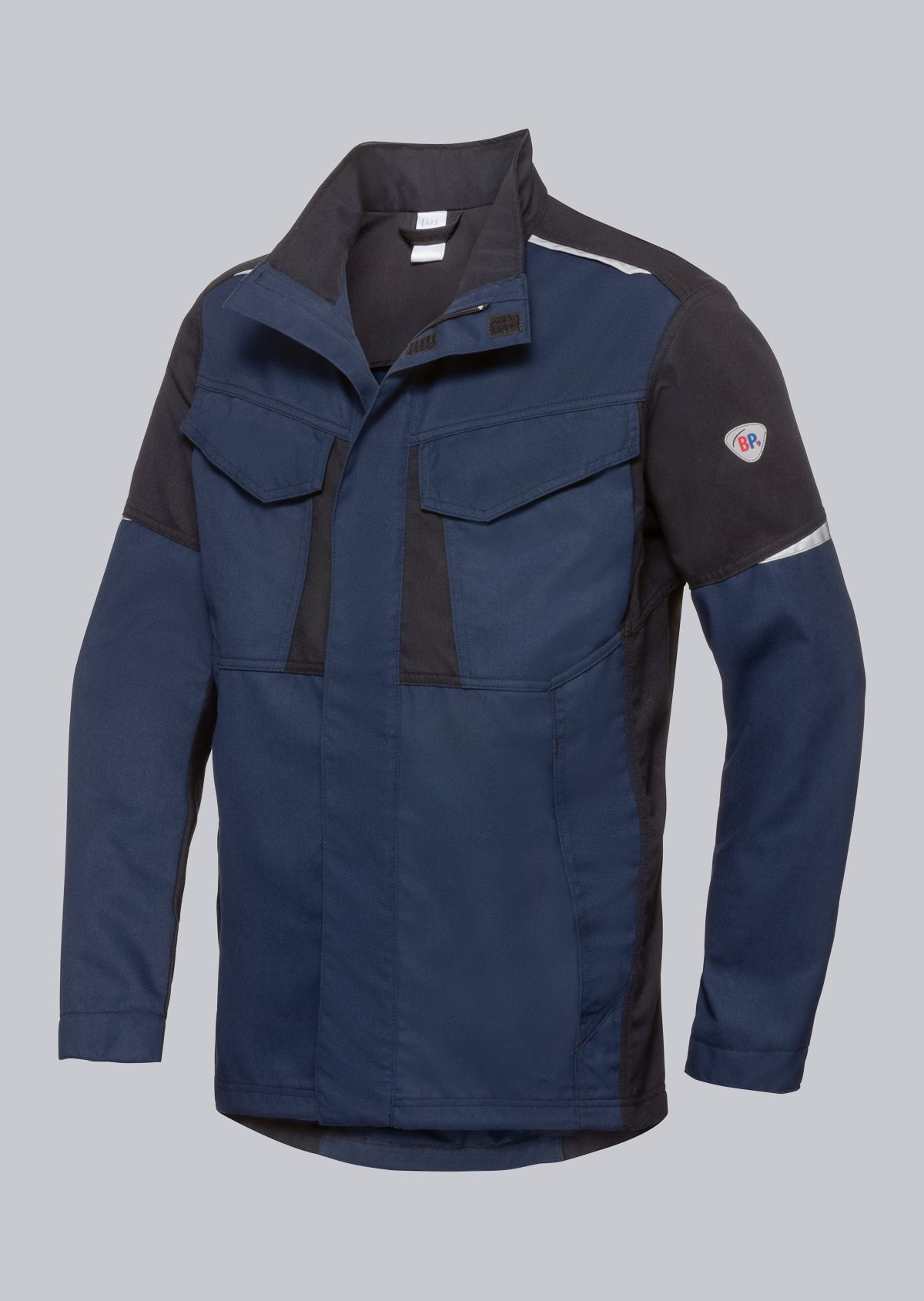
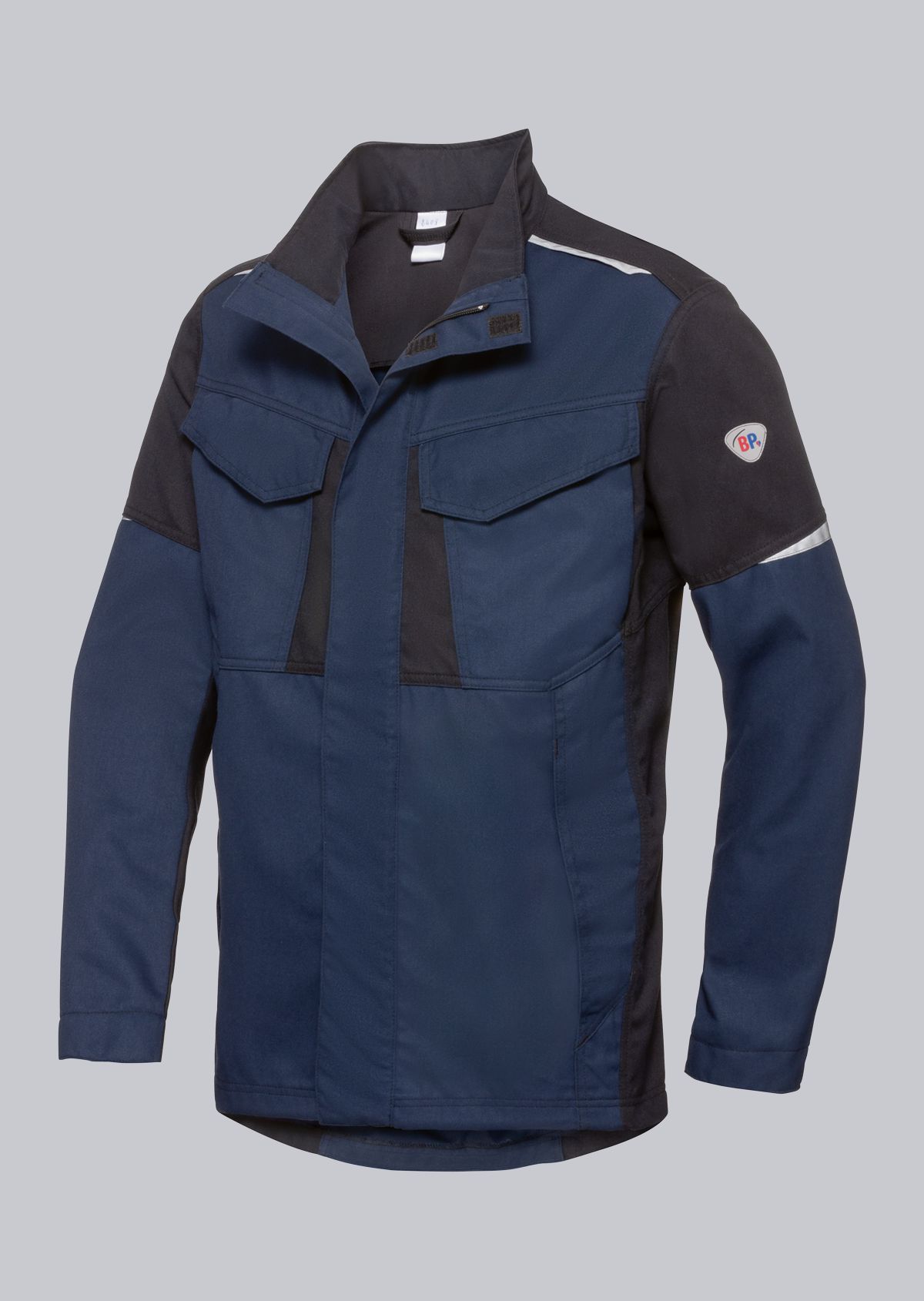
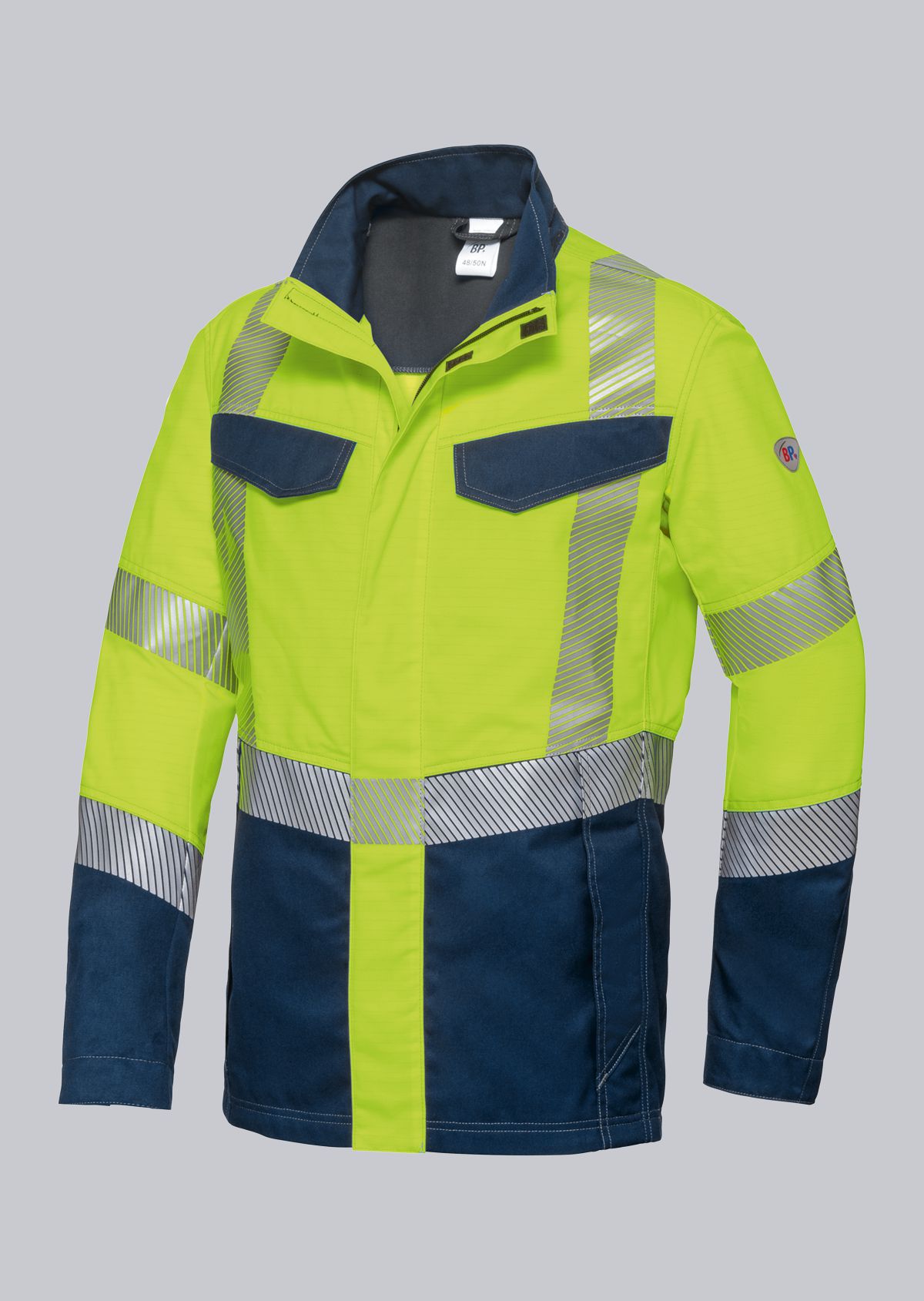
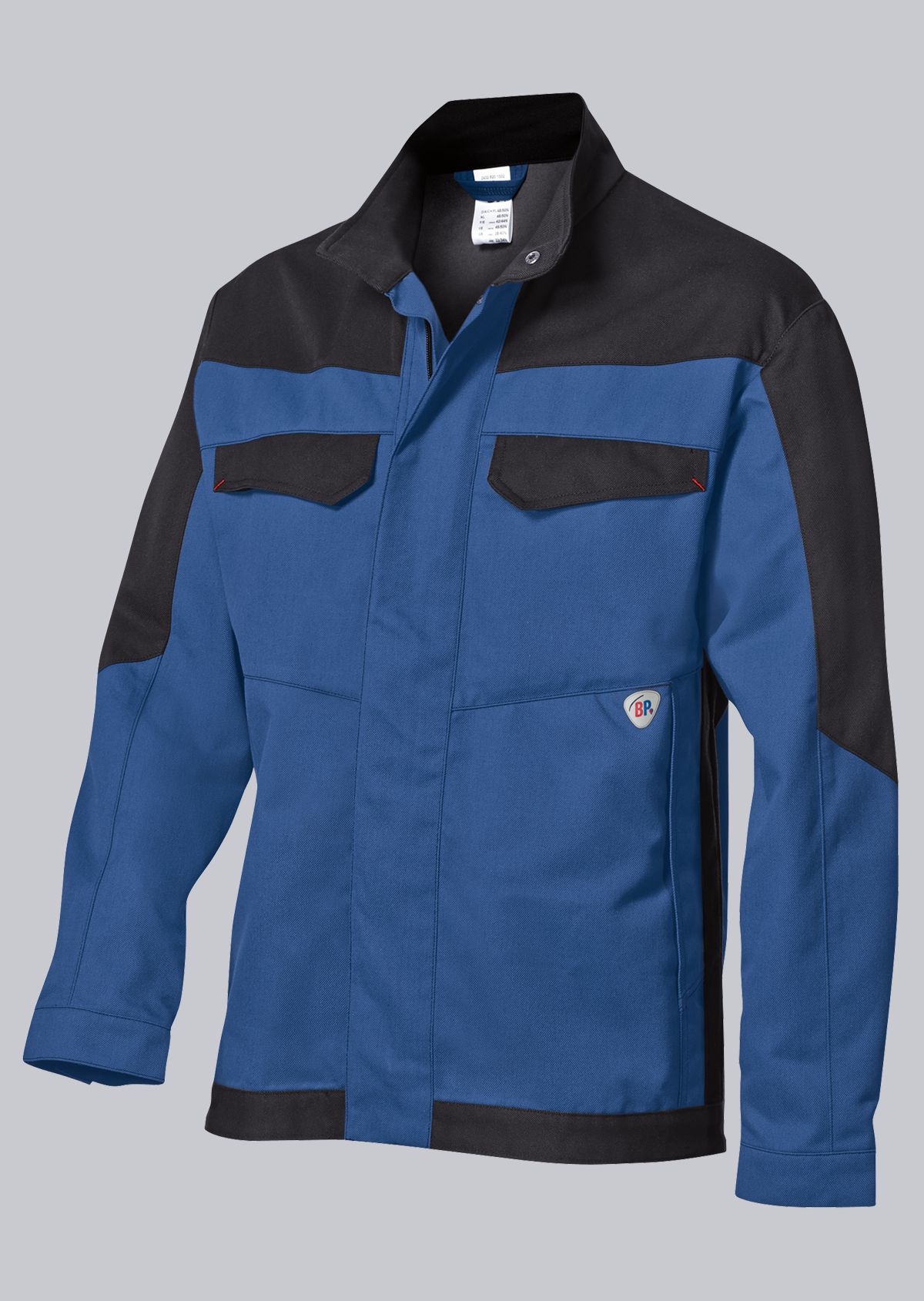
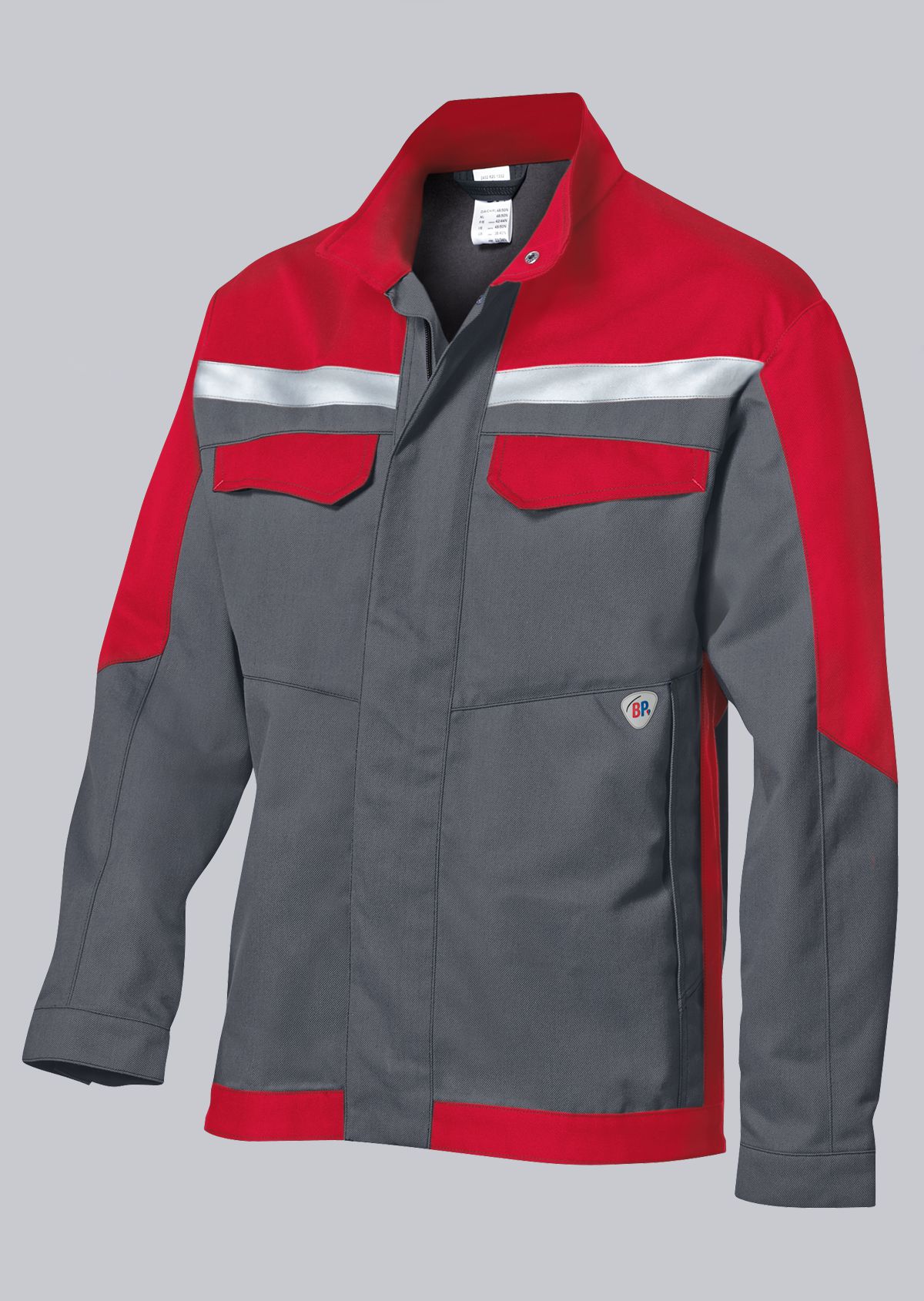
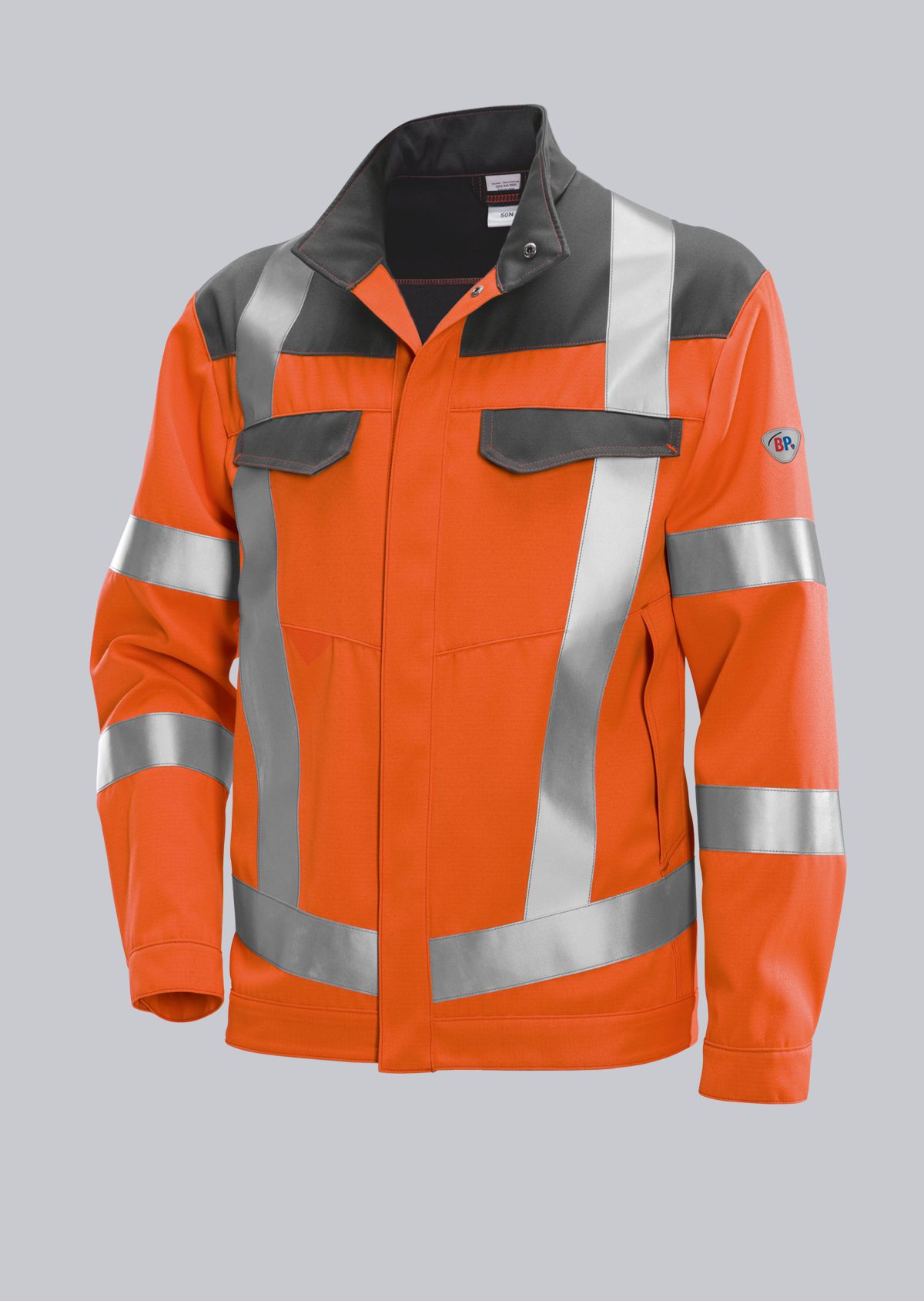
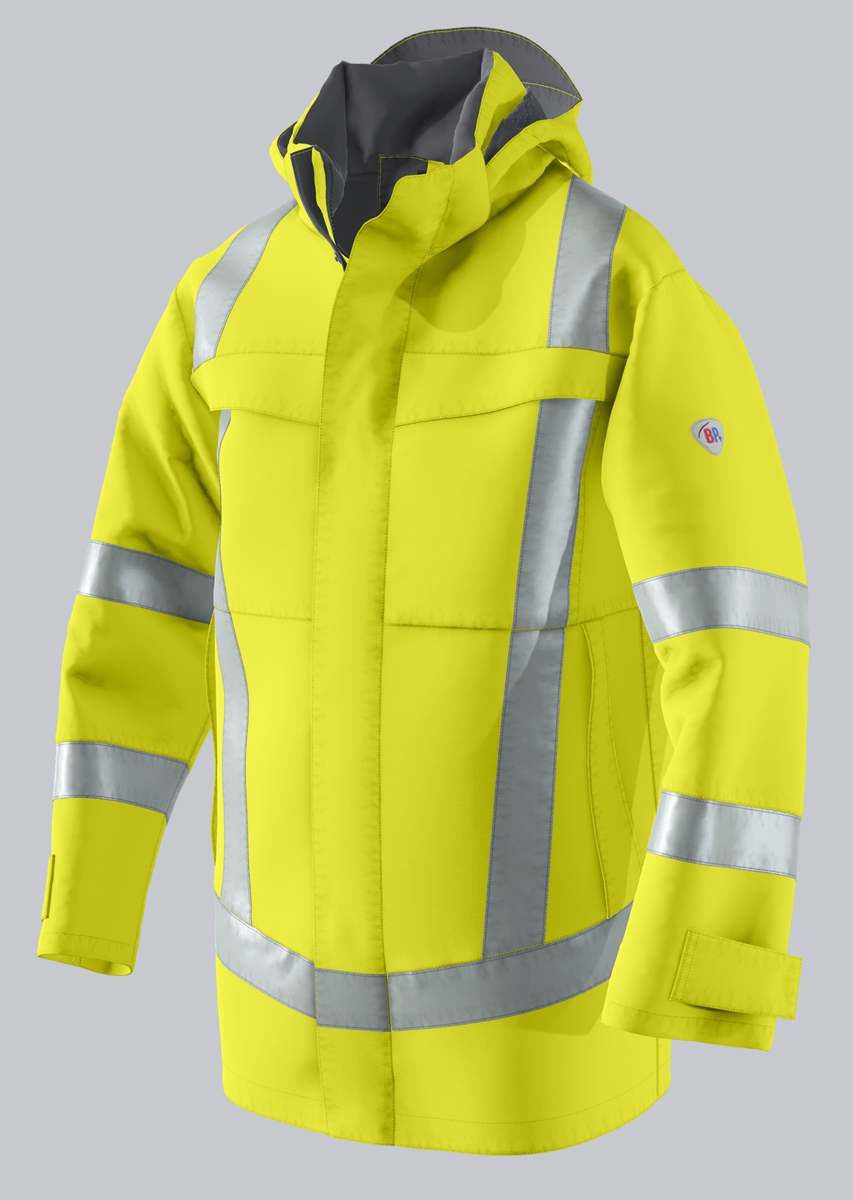
Work jackets according to EN ISO 11611
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective equipment here.
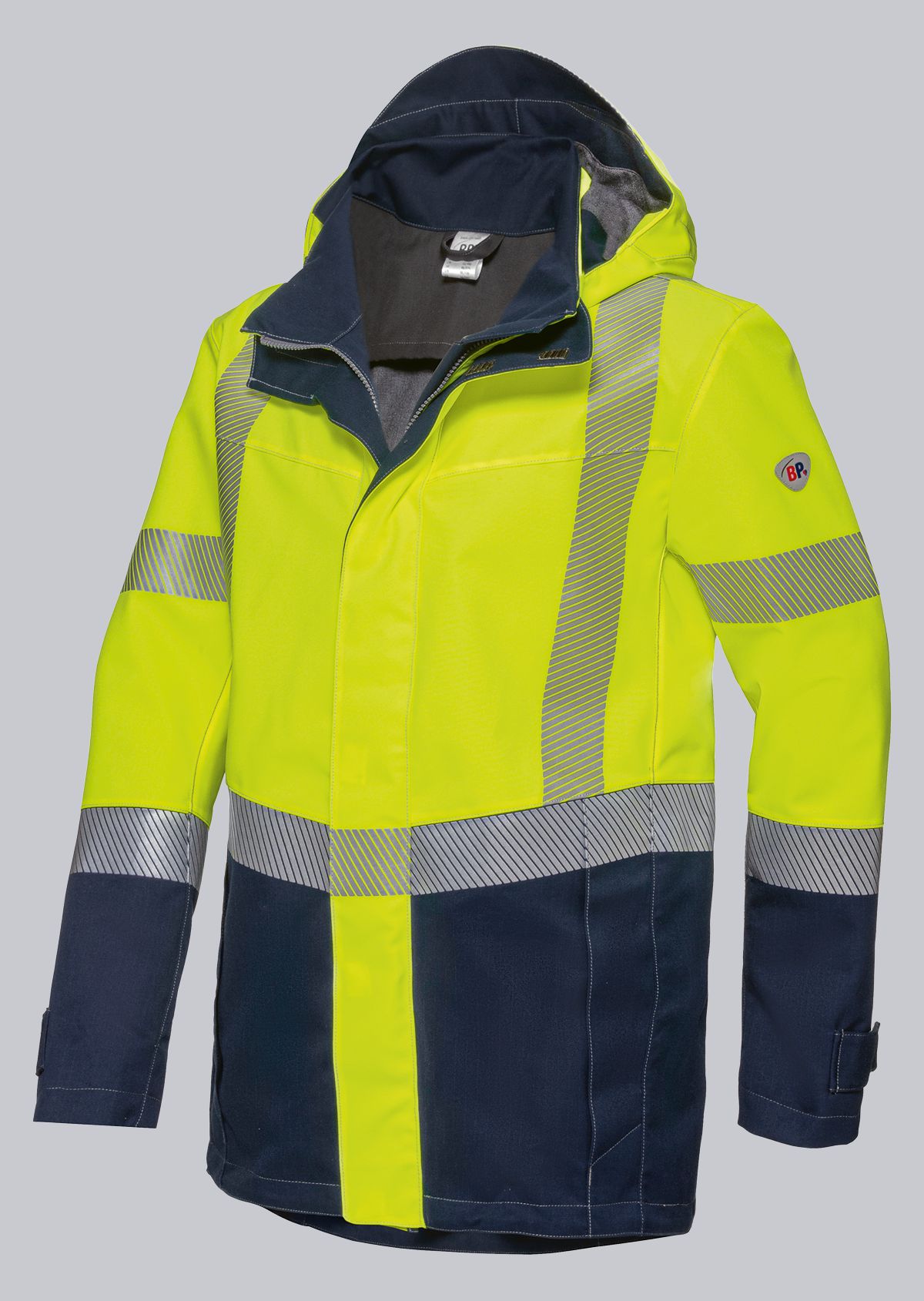
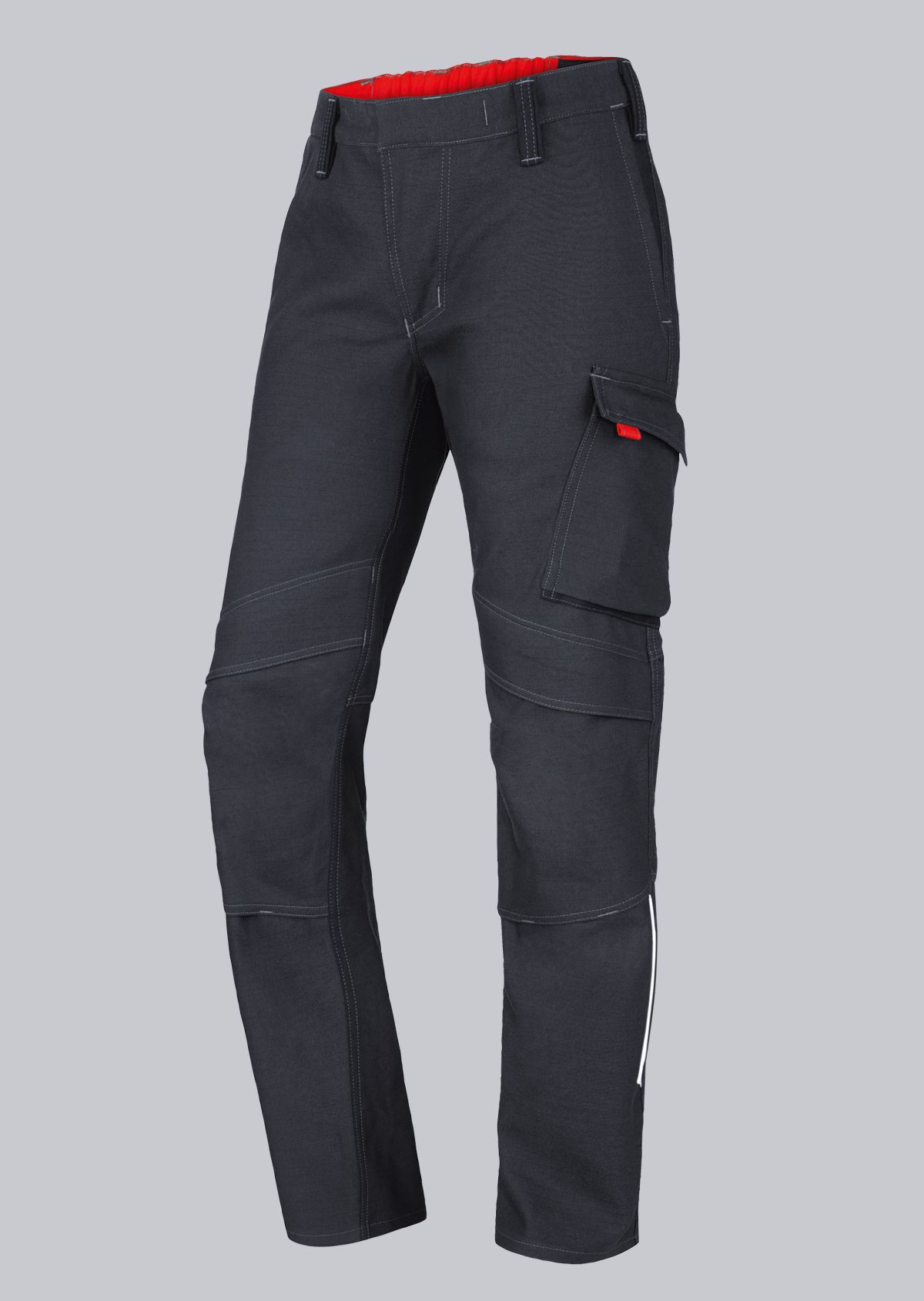
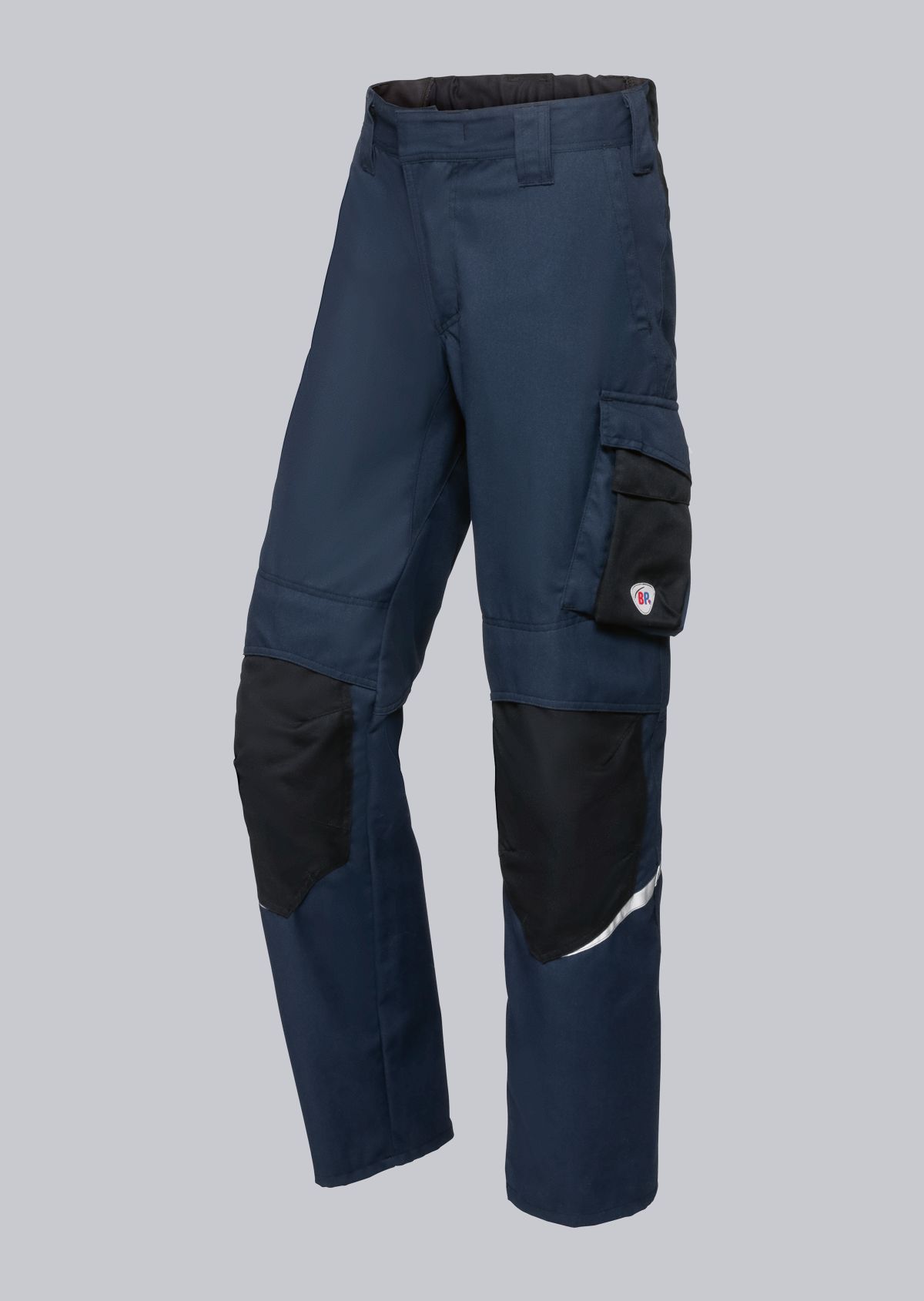
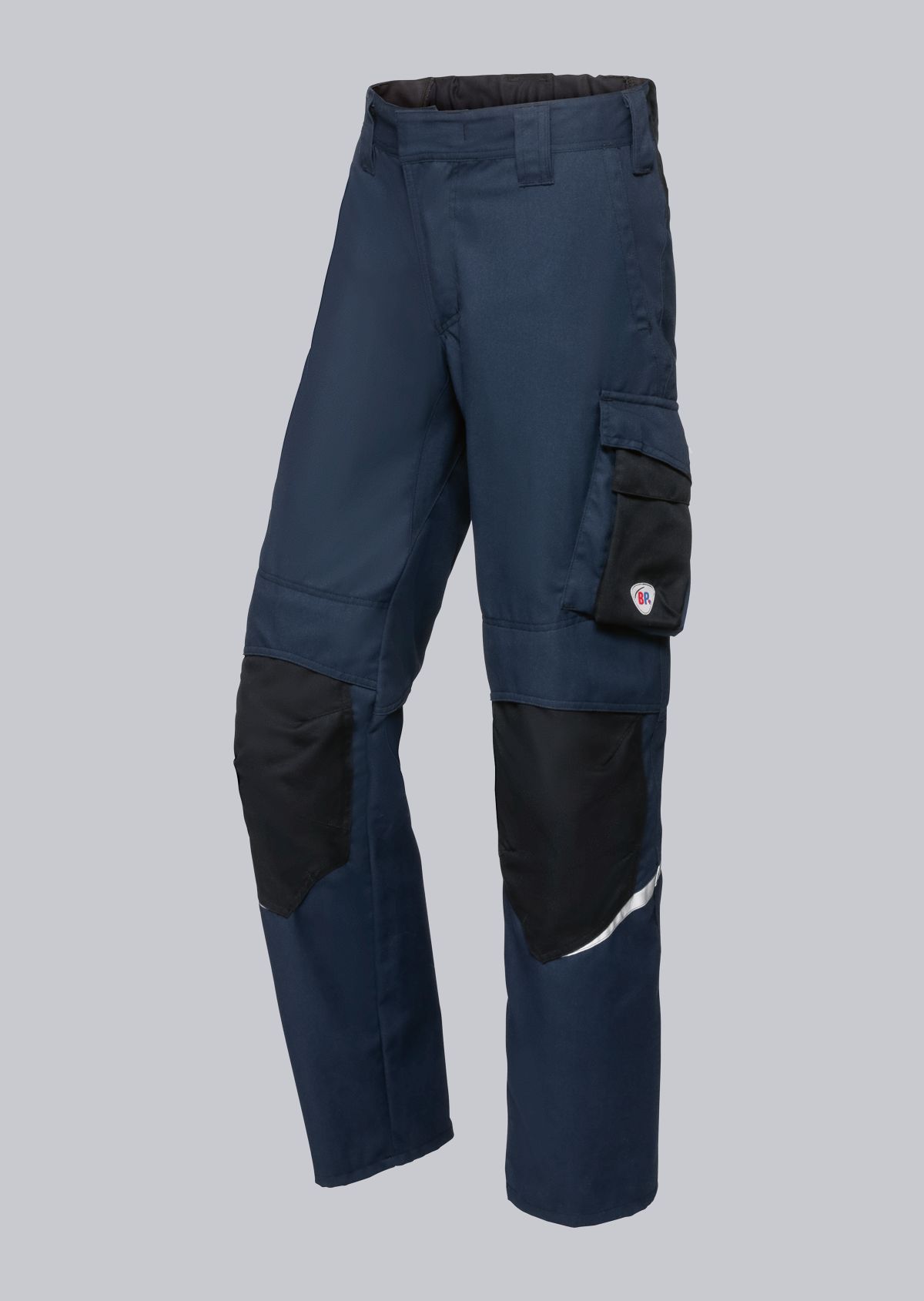
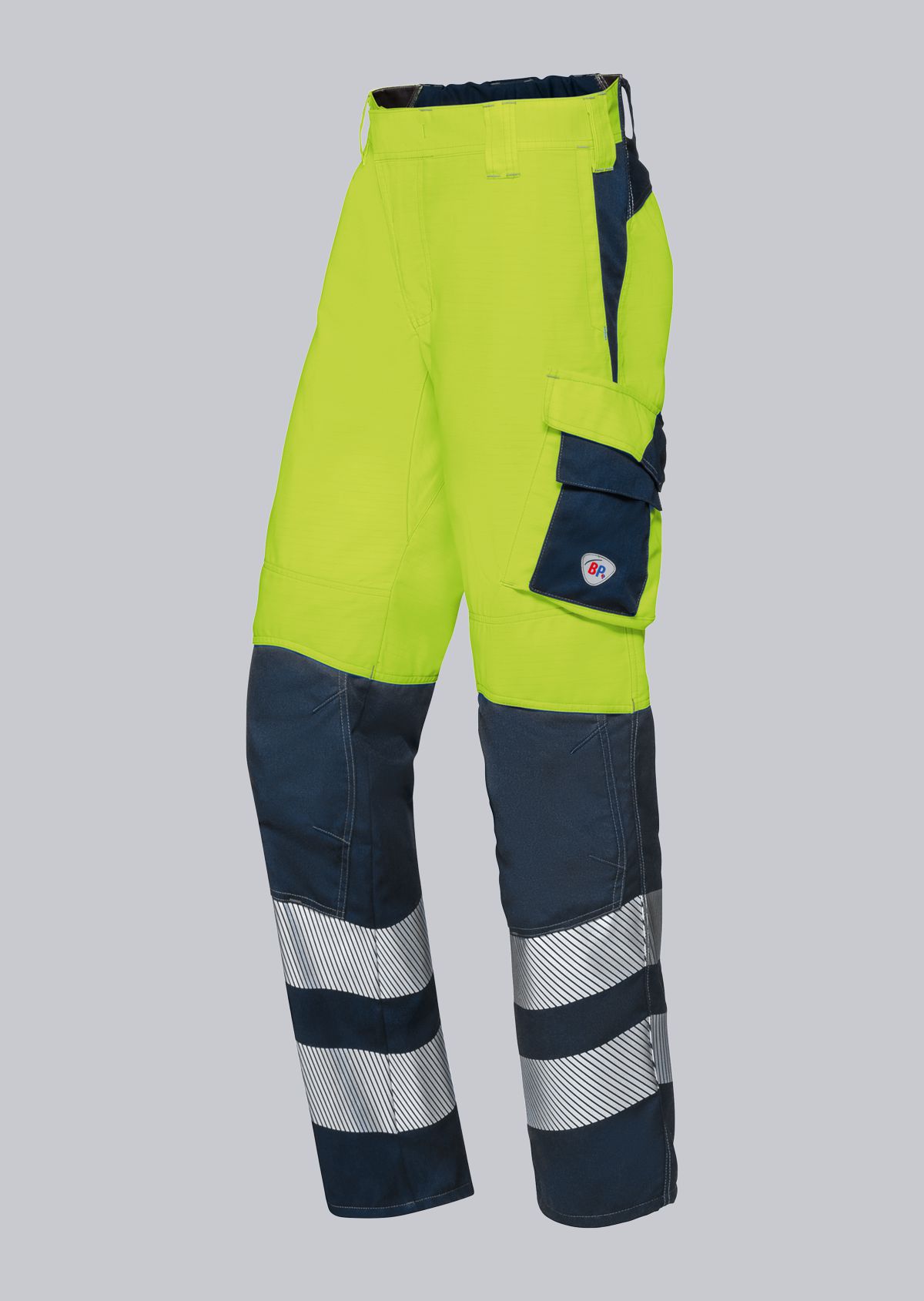
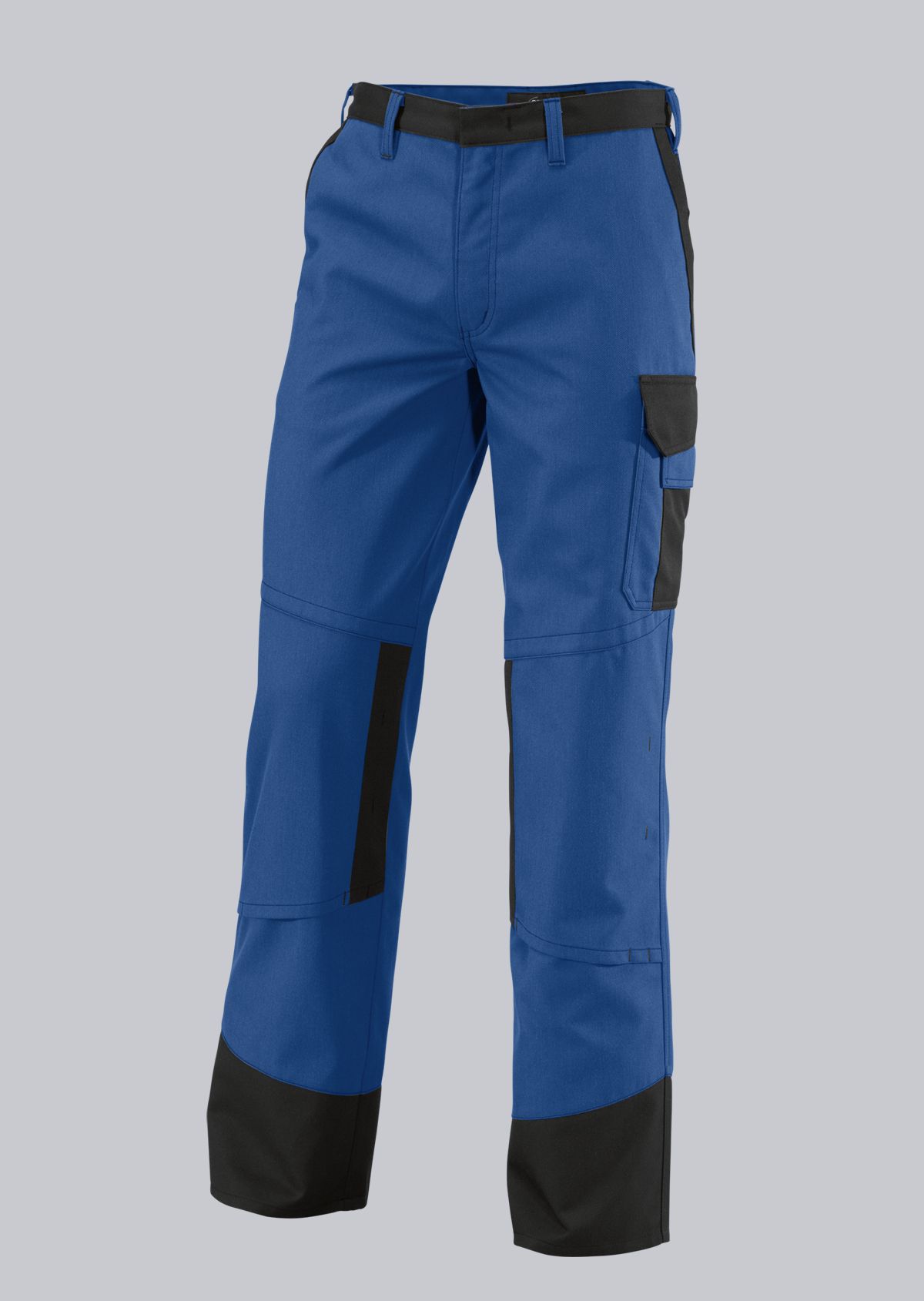
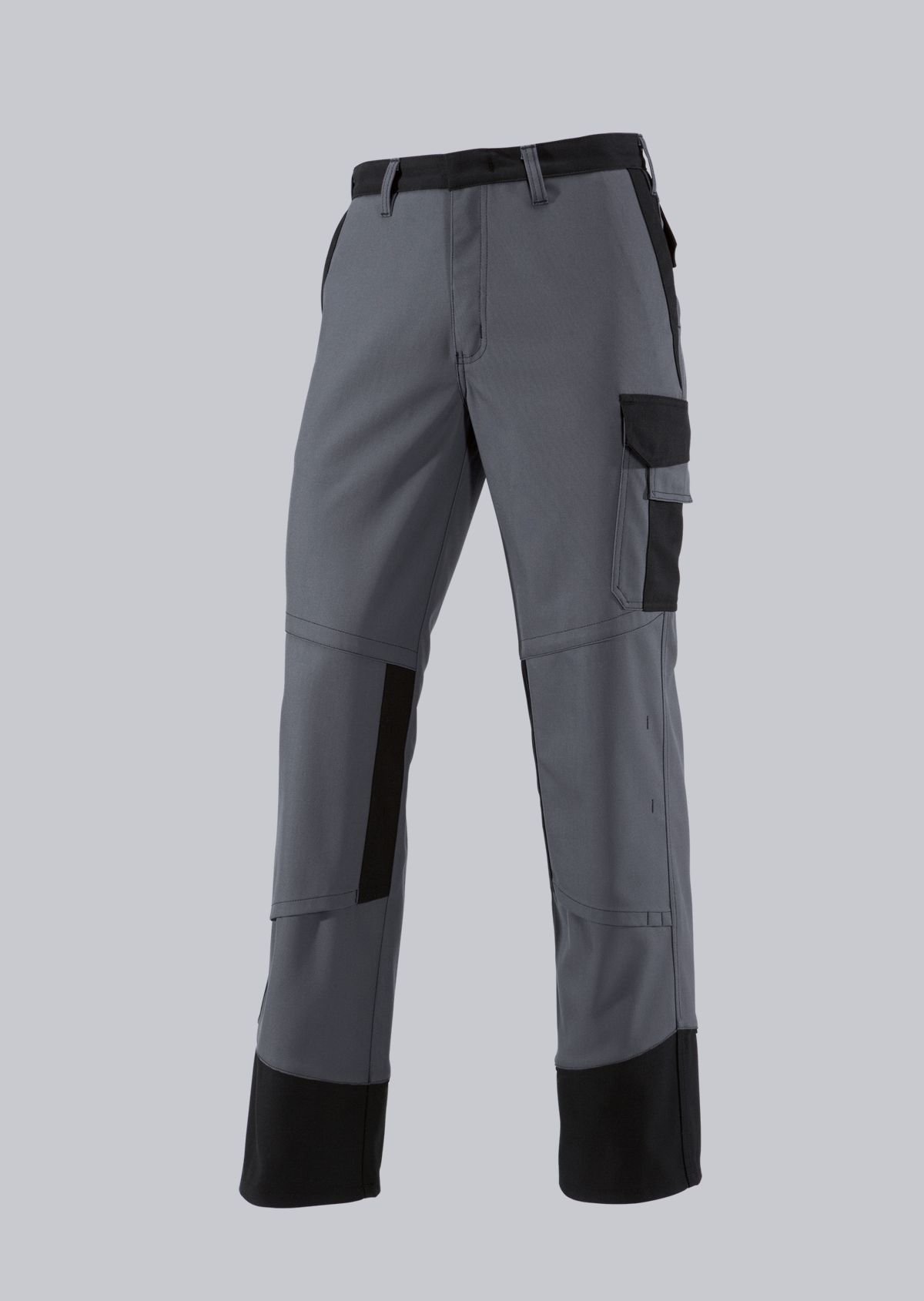
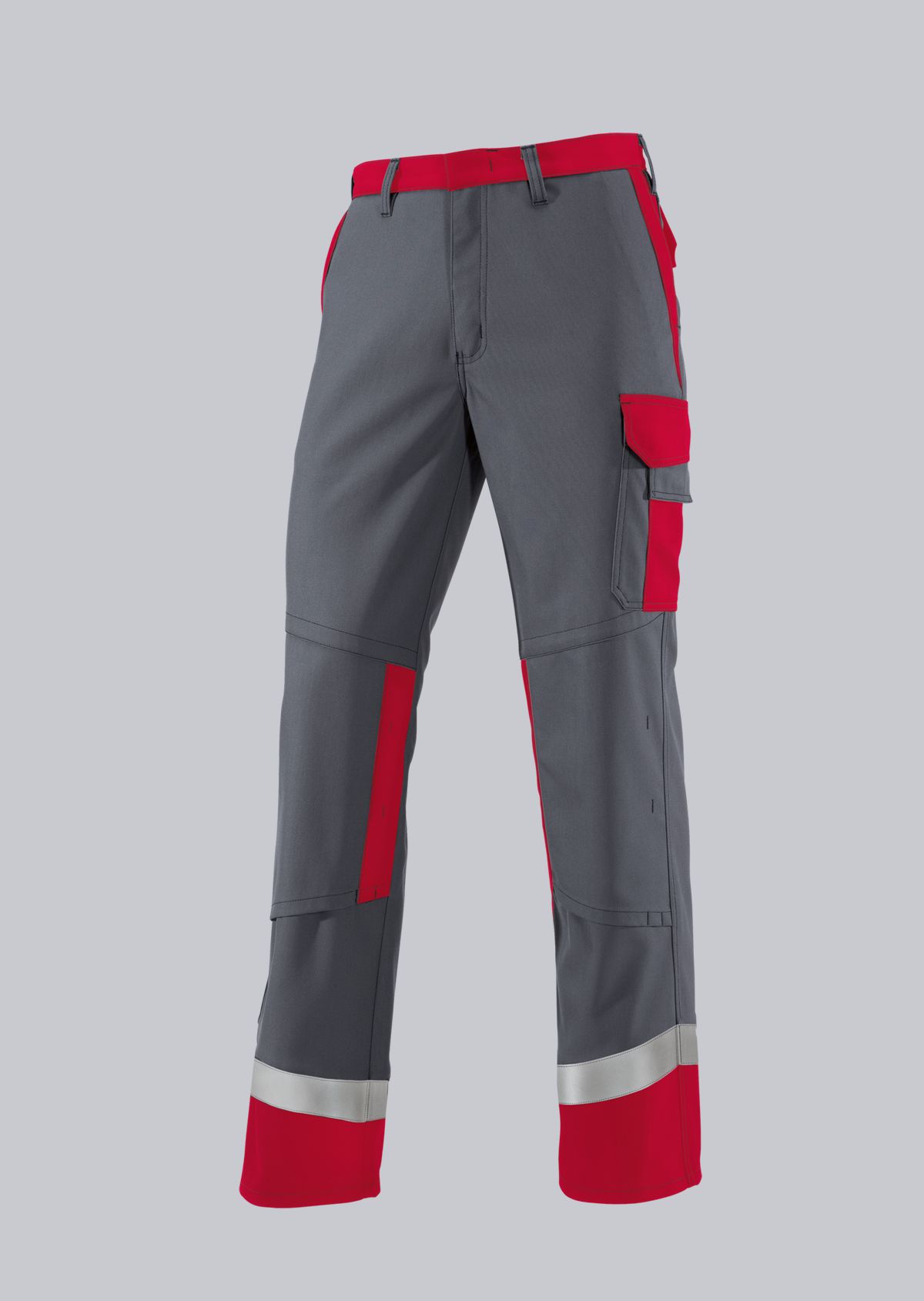
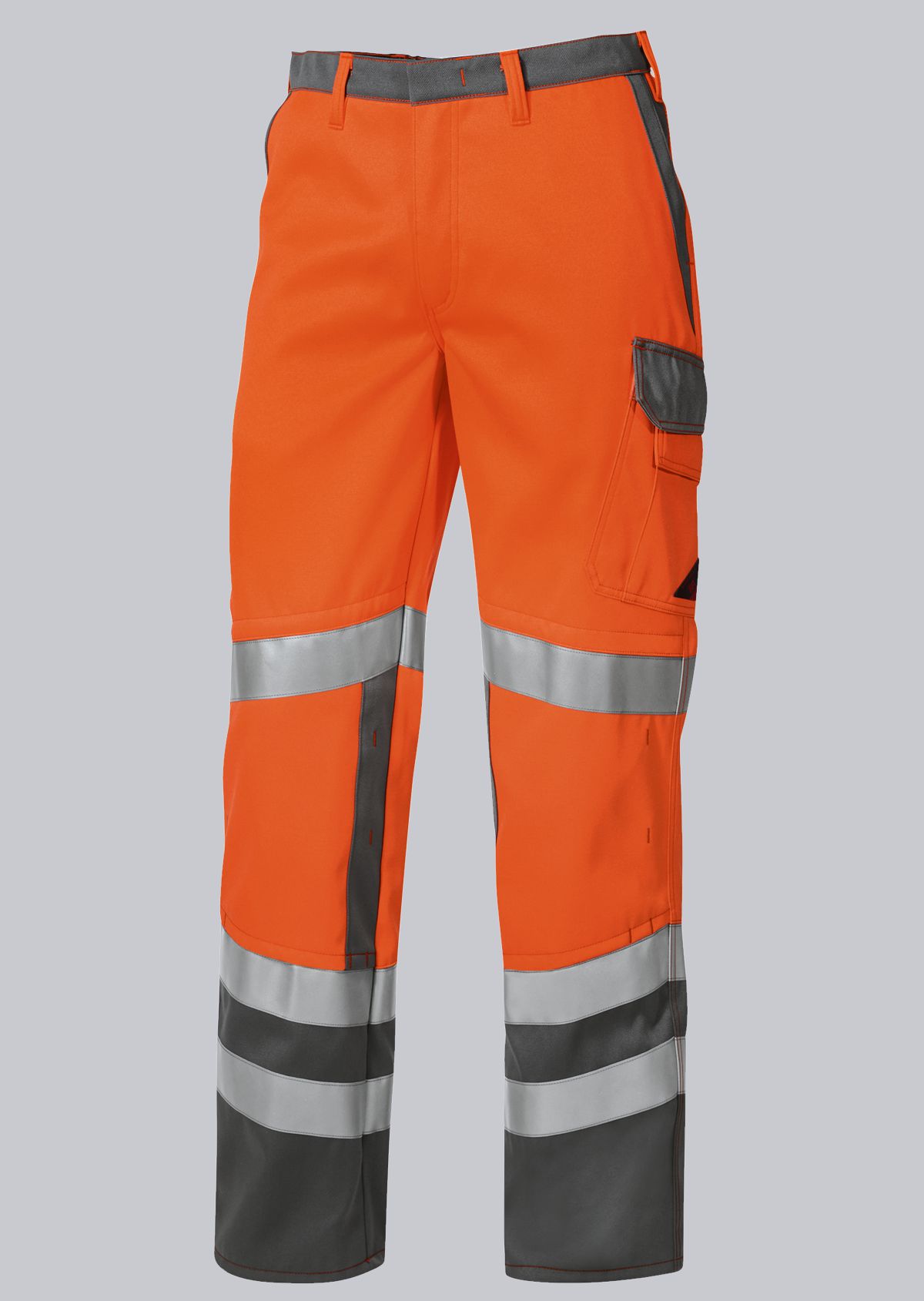
Trousers according to EN ISO 11611
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective equipment here.
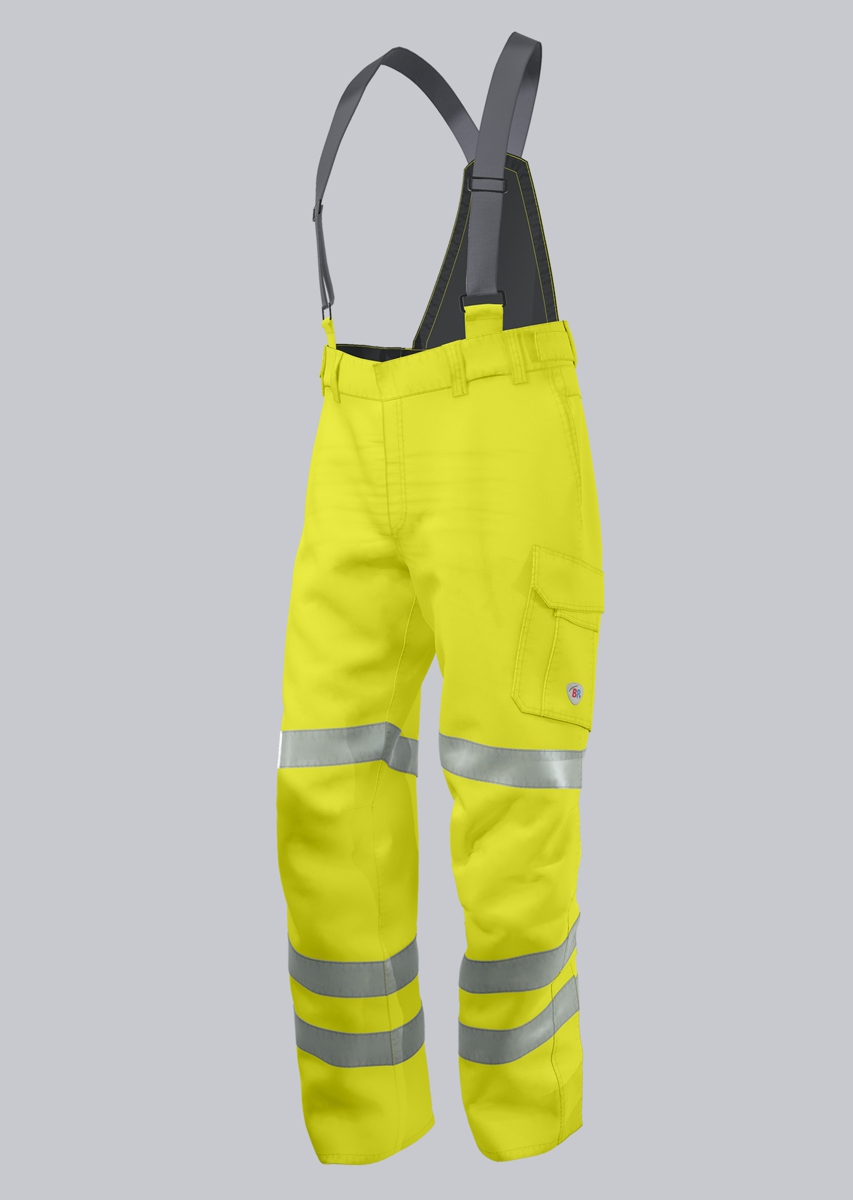
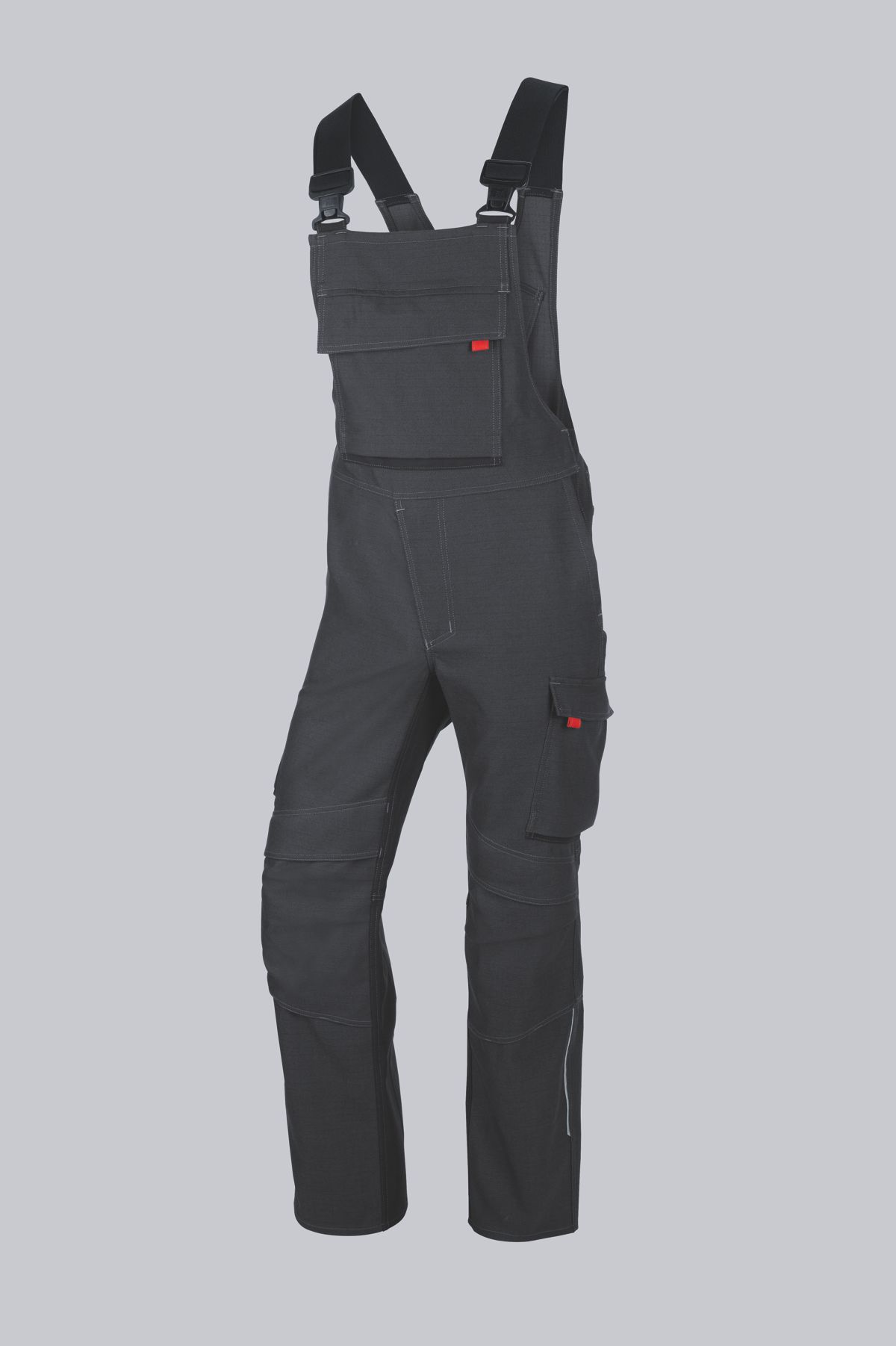
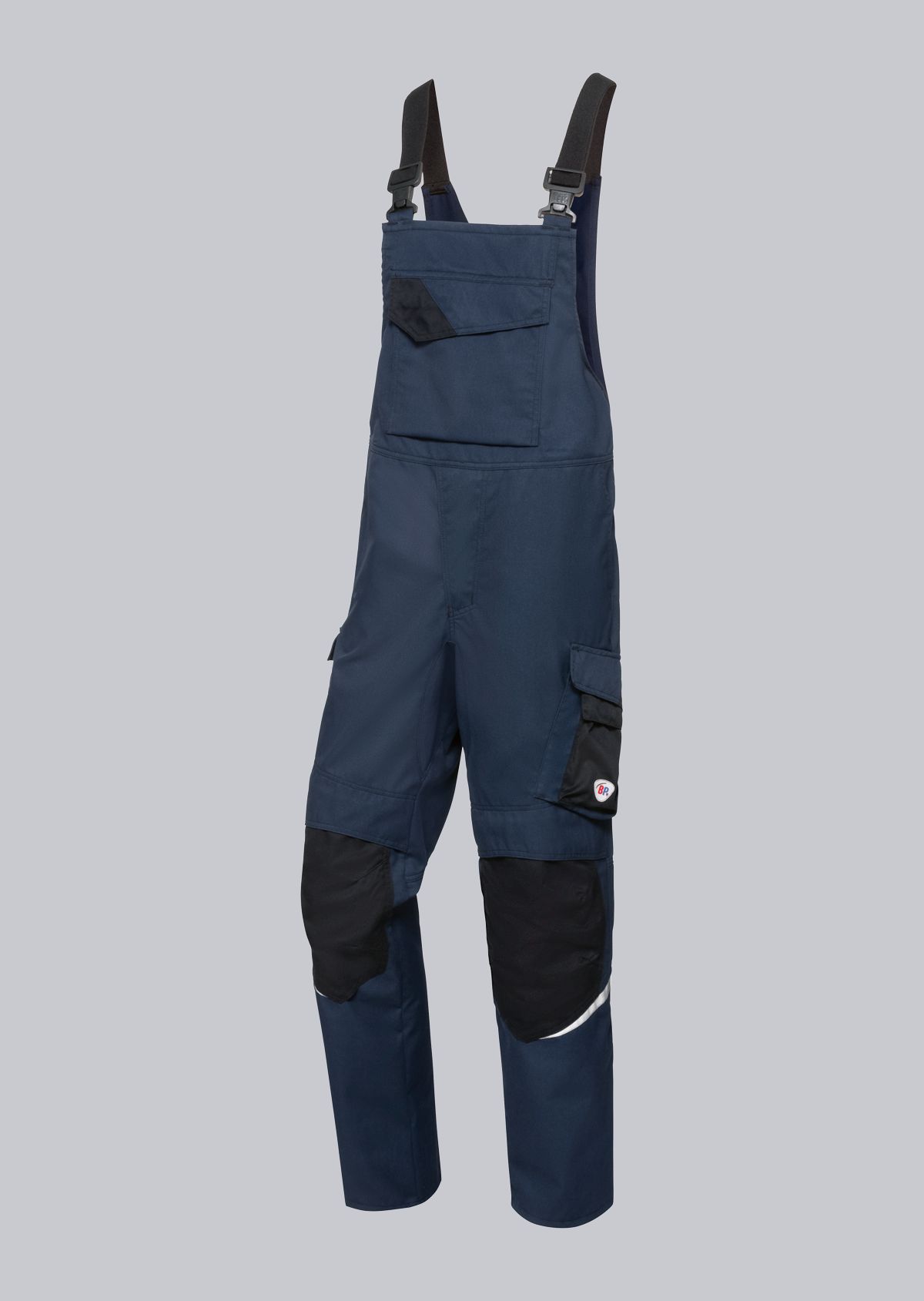
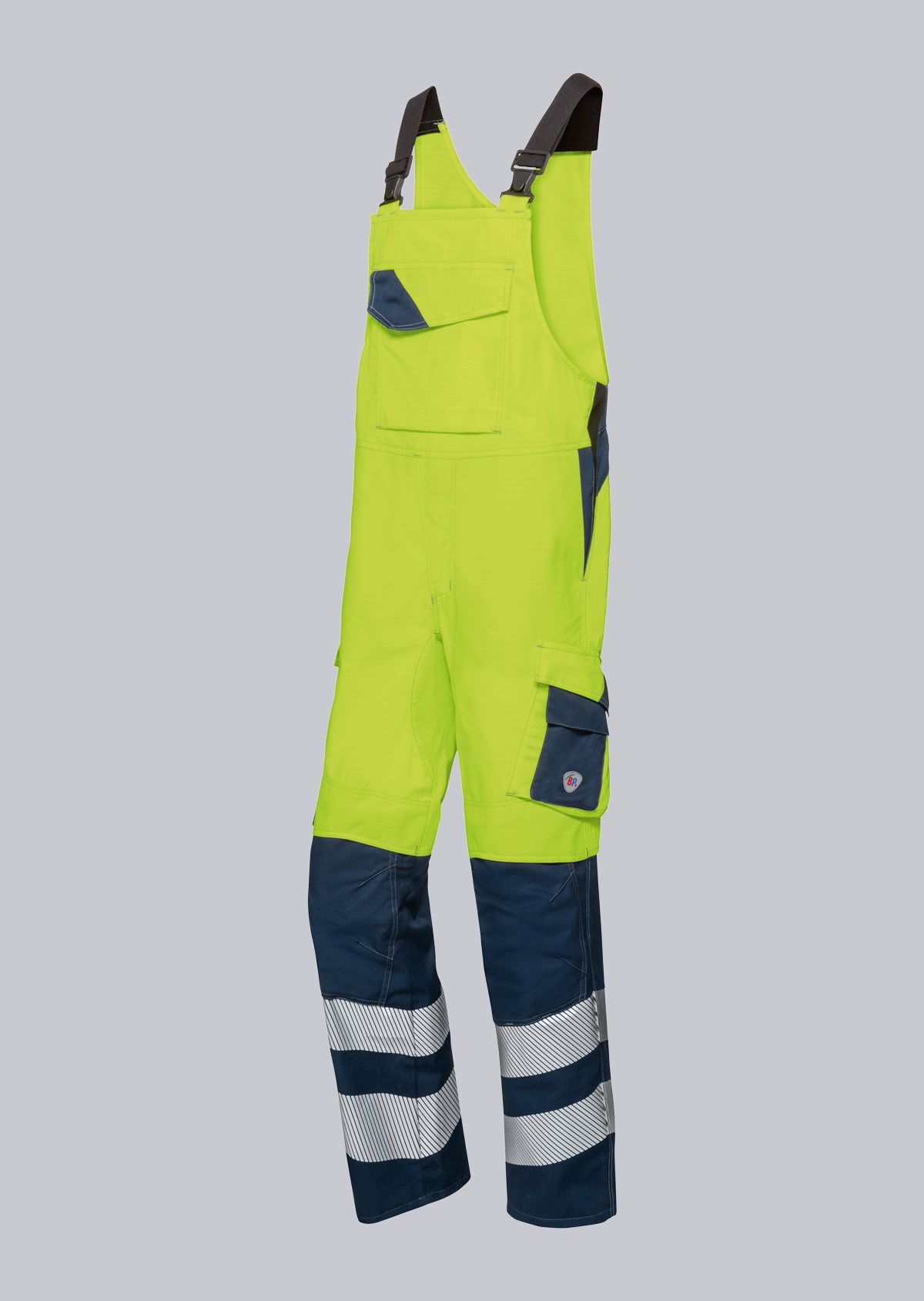
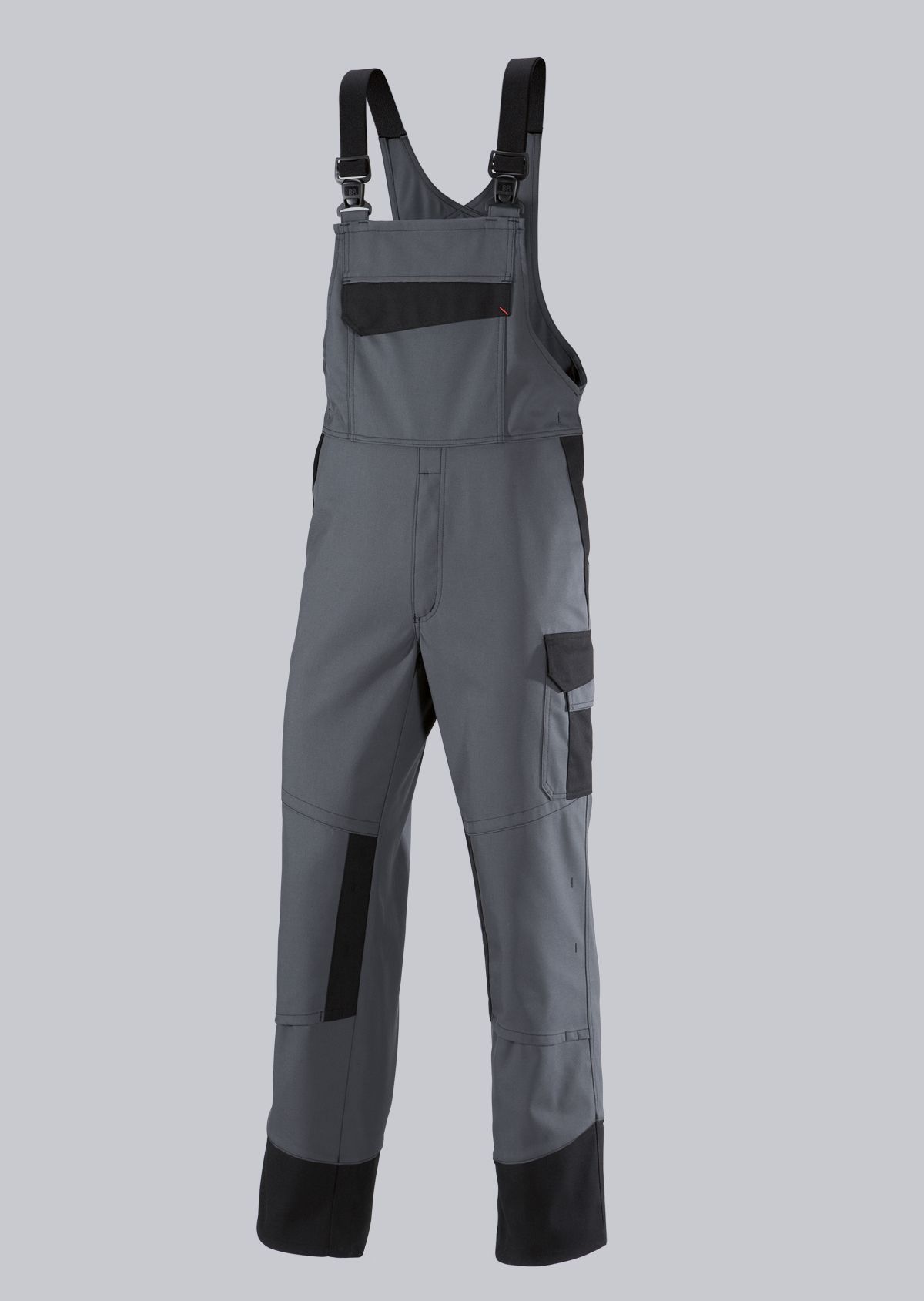
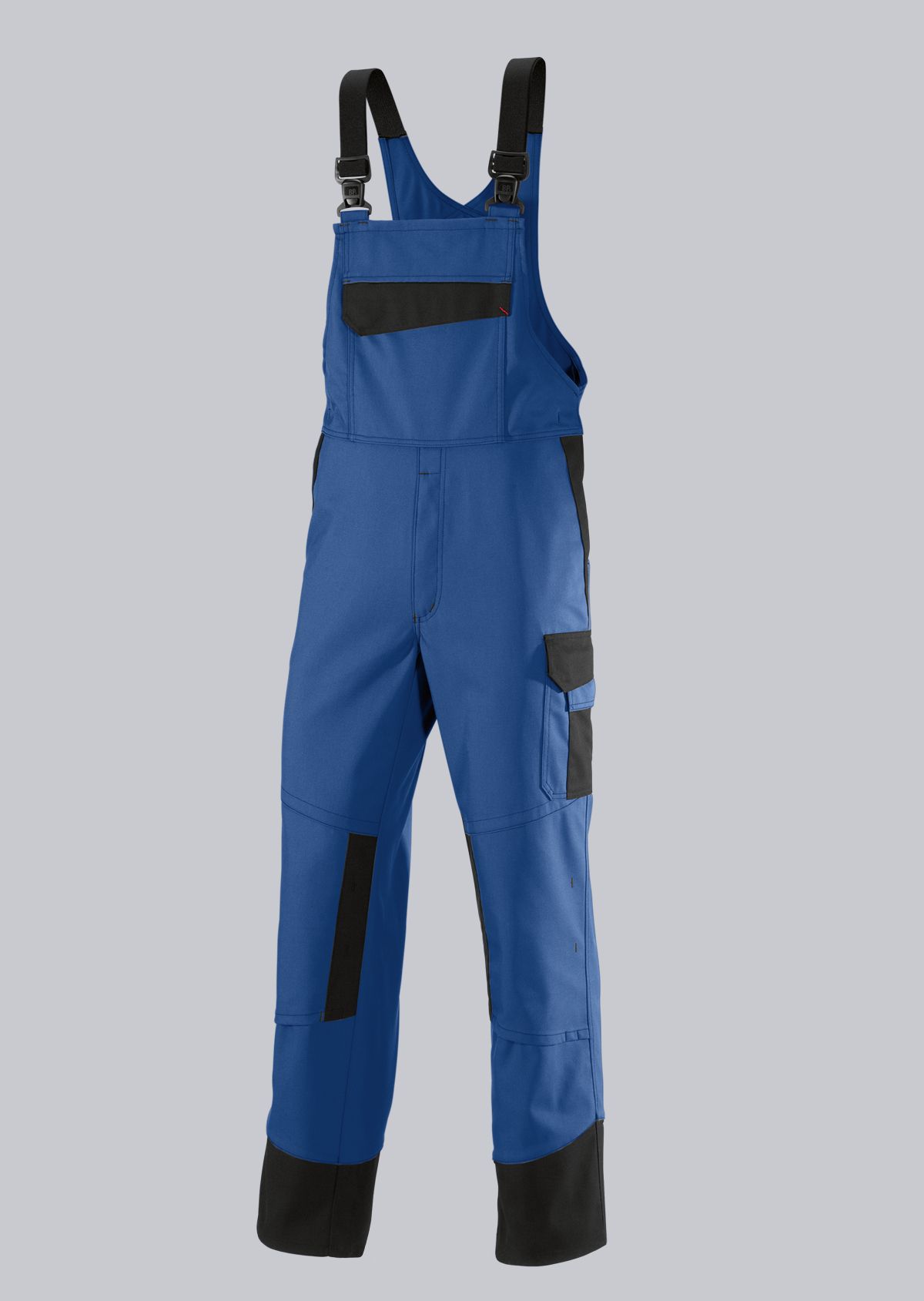
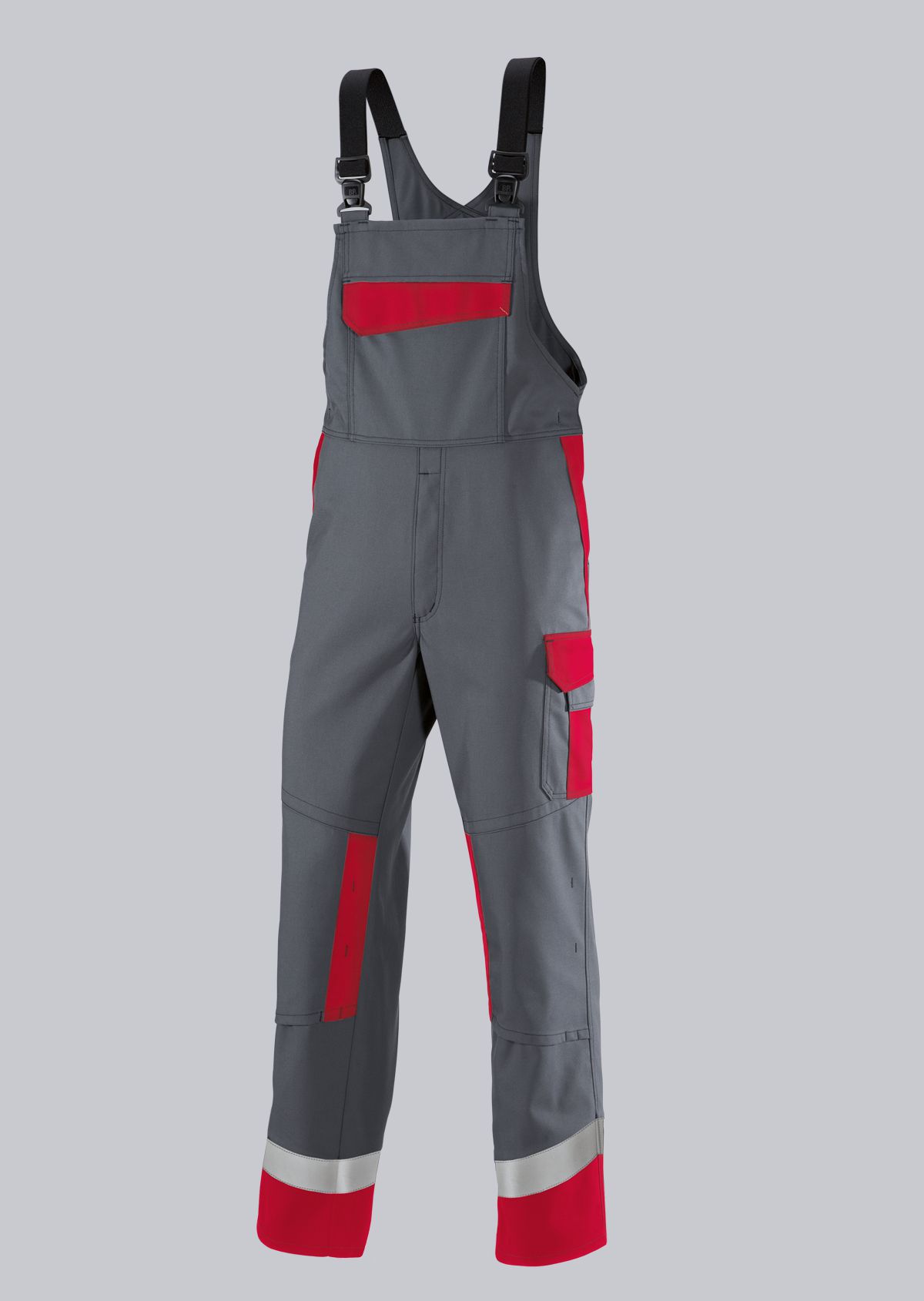
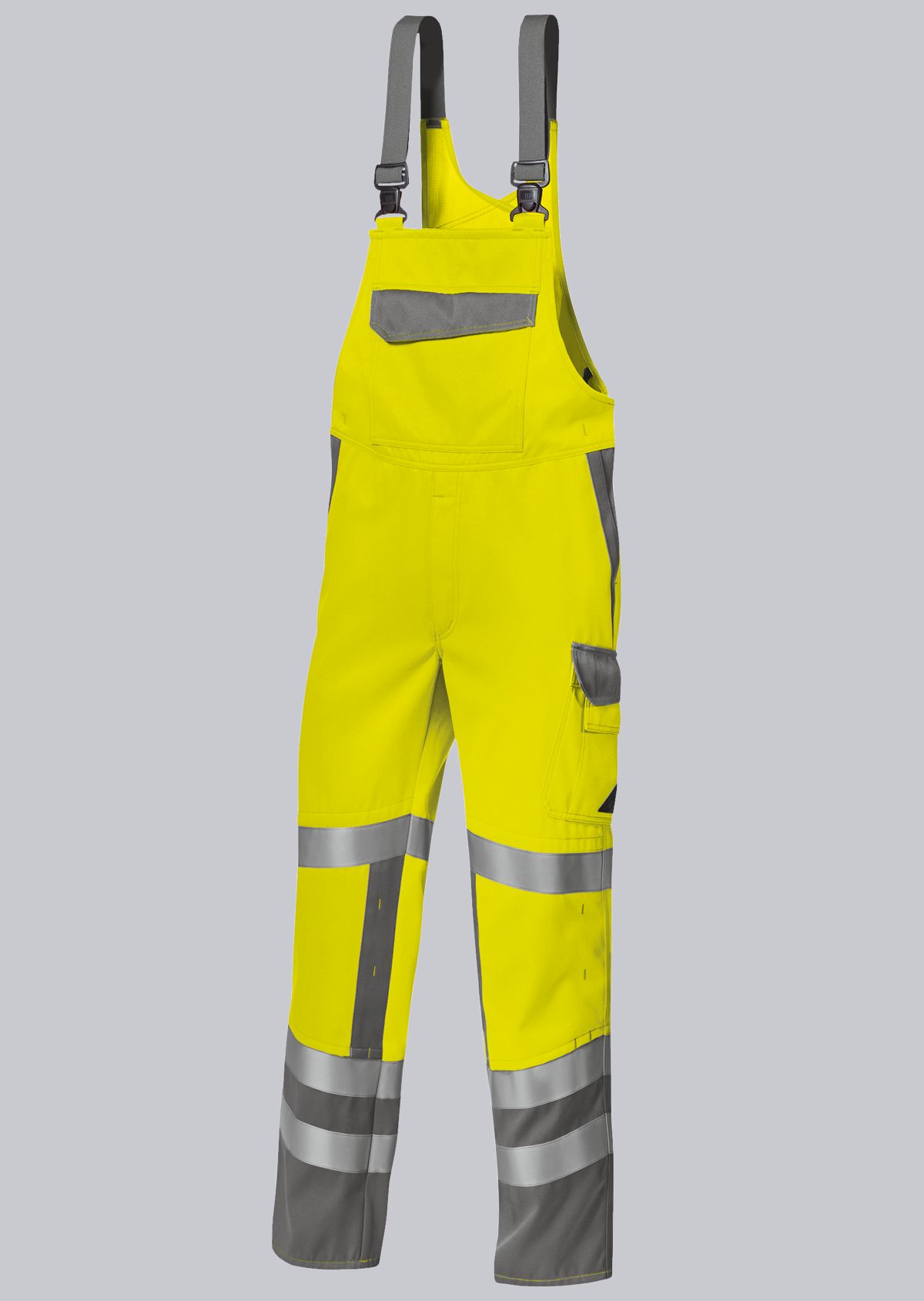
Bib & Braces according to EN ISO 11611
You will find a small selection of standard-compliant protective equipment here.
BP® NEWSLETTER
SPECIAL OFFERS, PROMOTIONS, NEW PRODUCTS AND MUCH MORE
Subscribe to our newsletter now and you'll be the first to receive all the information about sales promotions, new products or special online offers.
Subscribe to newsletter

Overline
TEAM EQUIPMENT REQUIRED?
You want to equip an entire team or company with PPE and need support in selecting and compiling protective clothing that conforms to standards?
CONTACT US



































.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)